Wood industry
The wood industry encompasses a wide range of activities related to the production, processing, and distribution of wood and wood products. This includes activities such as forestry, logging, sawmilling, woodworking, wood processing, and the manufacturing of various wood products such as lumber, plywood, furniture, paper, and more. The wood industry plays a crucial role in various sectors including construction, furniture manufacturing, packaging, and renewable energy. It involves both the sustainable management of forests and the utilization of wood resources to meet the demand for various products.
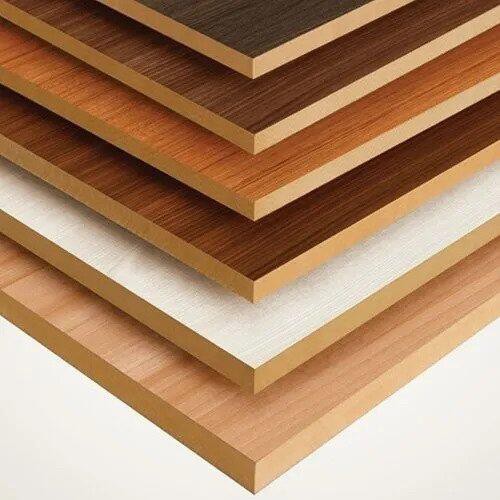
Wood products refer to a wide range of items made from wood or wood-based materials. These products serve various purposes in construction, furniture making, packaging, and other industries.
Some common wood products include:
1. Lumber: Wooden boards and planks used in construction and woodworking projects.
2. Plywood: Engineered wood product made from thin layers of wood veneer glued together.
3. Furniture: Wooden furniture items such as tables, chairs, cabinets, and beds.
4. Flooring: Wooden flooring materials including hardwood, laminate, and engineered wood.
5. Doors and Windows: Wooden doors, windows, and frames used in construction.
6. Paper and Pulp: Paper products made from wood pulp, including newspapers, magazines, and packaging materials.
7. Wood Pellets: Compressed wood particles used as a renewable energy source for heating and cooking.
8. Wood Chips and Mulch: Wooden chips and mulch used for landscaping, gardening, and erosion control.
9. Wooden Toys and Crafts: Handcrafted wooden toys, decorations, and artistic items.
10. Wood-Based Panels: Panels made from wood particles or fibers, including particleboard, fiberboard, and oriented strand board (OSB).
These are just a few examples of wood products, and the wood industry continues to innovate and develop new products to meet the needs of various sectors.
Wood forestry, also known as forestry or silviculture, is the practice of managing forested areas for the sustainable production of timber and other forest products. It involves various activities such as:
1. Reforestation and Afforestation: Planting new trees to replace harvested ones or establishing forests on previously non-forested land.
2. Timber Harvesting: Selectively harvesting mature trees for timber production while ensuring the regeneration of the forest.
3. Thinning: Removing some trees from overcrowded stands to promote the growth of remaining trees and improve forest health.
4. Fire Management: Implementing measures to prevent and control wildfires, which can damage forests and disrupt ecosystem functions.
5. Pest and Disease Management: Monitoring and managing pests and diseases that can affect forest health and productivity.
6. Wildlife Habitat Management: Maintaining and enhancing habitats for wildlife species that depend on forest ecosystems.
7. Soil and Water Conservation: Implementing practices to minimize soil erosion, protect water quality, and maintain healthy forest soils.
8. Forest Certification: Obtaining certification from independent organizations to demonstrate adherence to sustainable forestry practices.
9. Community Engagement: Involving local communities in forest management decisions and ensuring their participation in the benefits derived from forest resources.
_1710351276.jpg)
Wood forestry aims to balance the economic, environmental, and social aspects of forest management to ensure the long-term sustainability of forest ecosystems and the continued provision of wood and other forest products.
Wood logging, also known as timber harvesting or timber extraction, is the process of cutting down trees for commercial purposes, primarily for the production of wood products such as lumber, paper, and pulp. Logging operations can vary widely in scale, from small-scale selective logging to large-scale clear-cutting operations.
The process of wood logging typically involves the following steps:
1. Tree Selection: Depending on the objectives of the logging operation and the forest management plan in place, trees may be selected for harvesting based on factors such as species, size, and quality.
2. Tree Felling: Once selected, trees are cut down using various methods, including chainsaws, mechanical harvesters, or even manual labor in some cases.
3. Tree Extraction: After felling, the trees are typically transported from the forest to a central location, known as a log landing or log deck, where they are processed further.
4. Processing: At the log landing, the trees may be delimbed (removing branches) and bucked (cut into manageable lengths) to prepare them for transportation to processing facilities.
5. Transportation: The harvested logs are then transported to sawmills, pulp mills, or other processing facilities using trucks, trailers, or in some cases, by floating them down rivers (known as log driving).
6. Processing and Utilization: At the processing facility, the logs are further processed into lumber, paper, or other wood products based on their intended use.
7. Reforestation: After harvesting, reforestation efforts may be undertaken to replant trees in the harvested areas to ensure the sustainable regeneration of the forest.
It's important to note that responsible logging practices aim to minimize environmental impacts, promote forest regeneration, and comply with relevant regulations and certification standards, such as those set forth by forestry certification programs like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) or the Sustainable Forestry Initiative (SFI).
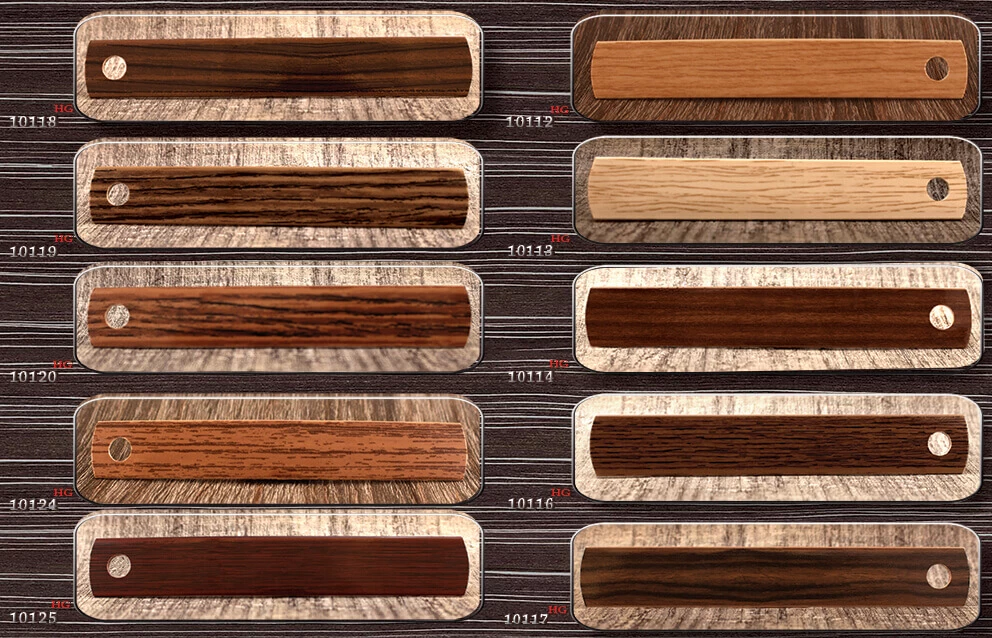
Edge banding is a process used in woodworking and furniture manufacturing to cover the exposed edges of plywood, particleboard, or other types of composite board with a thin strip of material, typically made of wood veneer, PVC, or ABS plastic. The purpose of edge banding is to provide a finished look to the edges of furniture components, as well as to protect them from moisture, chipping, and wear.


The edge banding process involves the following steps:
1. Preparation: The edges of the board to be edge banded are trimmed and smoothed to ensure they are clean and free of imperfections.
2. Selection of Edge Banding Material: Depending on the desired look and performance characteristics, a suitable edge banding material is selected. This can include wood veneer, PVC, ABS plastic, or even metal.
3. Application of Edge Banding: The edge banding material is applied to the edges of the board using a specialized edge banding machine. The machine applies heat and pressure to adhere the edge banding material to the edges of the board, ensuring a secure bond.
4. Trimming: Once the edge banding material is applied, any excess material is trimmed off using a trimming tool or edge banding trimmer to ensure a clean and flush edge.
5. Finishing: The edge-banded board is then sanded and finished to blend the edge banding seamlessly with the surface of the board, resulting in a smooth and uniform appearance.
Edge banding is commonly used in the manufacture of cabinets, countertops, shelving, and other furniture and cabinetry components to achieve a professional and polished look. It allows manufacturers to create durable and aesthetically pleasing products while also providing protection to the edges of the boards.
Wood products refer to a wide range of items made from wood or wood-based materials. These products serve various purposes in construction, furniture making, packaging, and other industries.
2. Plywood: Engineered wood product made from thin layers of wood veneer glued together.
3. Furniture: Wooden furniture items such as tables, chairs, cabinets, and beds.
4. Flooring: Wooden flooring materials including hardwood, laminate, and engineered wood.
5. Doors and Windows: Wooden doors, windows, and frames used in construction.
6. Paper and Pulp: Paper products made from wood pulp, including newspapers, magazines, and packaging materials.
7. Wood Pellets: Compressed wood particles used as a renewable energy source for heating and cooking.
8. Wood Chips and Mulch: Wooden chips and mulch used for landscaping, gardening, and erosion control.
9. Wooden Toys and Crafts: Handcrafted wooden toys, decorations, and artistic items.
10. Wood-Based Panels: Panels made from wood particles or fibers, including particleboard, fiberboard, and oriented strand board (OSB).
Wood forestry, also known as forestry or silviculture, is the practice of managing forested areas for the sustainable production of timber and other forest products. It involves various activities such as:
1. Reforestation and Afforestation: Planting new trees to replace harvested ones or establishing forests on previously non-forested land.
2. Timber Harvesting: Selectively harvesting mature trees for timber production while ensuring the regeneration of the forest.
3. Thinning: Removing some trees from overcrowded stands to promote the growth of remaining trees and improve forest health.
4. Fire Management: Implementing measures to prevent and control wildfires, which can damage forests and disrupt ecosystem functions.
5. Pest and Disease Management: Monitoring and managing pests and diseases that can affect forest health and productivity.
6. Wildlife Habitat Management: Maintaining and enhancing habitats for wildlife species that depend on forest ecosystems.
7. Soil and Water Conservation: Implementing practices to minimize soil erosion, protect water quality, and maintain healthy forest soils.
8. Forest Certification: Obtaining certification from independent organizations to demonstrate adherence to sustainable forestry practices.
9. Community Engagement: Involving local communities in forest management decisions and ensuring their participation in the benefits derived from forest resources.
_1710351276.jpg)
Wood logging, also known as timber harvesting or timber extraction, is the process of cutting down trees for commercial purposes, primarily for the production of wood products such as lumber, paper, and pulp. Logging operations can vary widely in scale, from small-scale selective logging to large-scale clear-cutting operations.
The process of wood logging typically involves the following steps:
1. Tree Selection: Depending on the objectives of the logging operation and the forest management plan in place, trees may be selected for harvesting based on factors such as species, size, and quality.
2. Tree Felling: Once selected, trees are cut down using various methods, including chainsaws, mechanical harvesters, or even manual labor in some cases.
3. Tree Extraction: After felling, the trees are typically transported from the forest to a central location, known as a log landing or log deck, where they are processed further.
4. Processing: At the log landing, the trees may be delimbed (removing branches) and bucked (cut into manageable lengths) to prepare them for transportation to processing facilities.
5. Transportation: The harvested logs are then transported to sawmills, pulp mills, or other processing facilities using trucks, trailers, or in some cases, by floating them down rivers (known as log driving).
6. Processing and Utilization: At the processing facility, the logs are further processed into lumber, paper, or other wood products based on their intended use.
7. Reforestation: After harvesting, reforestation efforts may be undertaken to replant trees in the harvested areas to ensure the sustainable regeneration of the forest.
It's important to note that responsible logging practices aim to minimize environmental impacts, promote forest regeneration, and comply with relevant regulations and certification standards, such as those set forth by forestry certification programs like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) or the Sustainable Forestry Initiative (SFI).
Edge banding is a process used in woodworking and furniture manufacturing to cover the exposed edges of plywood, particleboard, or other types of composite board with a thin strip of material, typically made of wood veneer, PVC, or ABS plastic. The purpose of edge banding is to provide a finished look to the edges of furniture components, as well as to protect them from moisture, chipping, and wear.


1. Preparation: The edges of the board to be edge banded are trimmed and smoothed to ensure they are clean and free of imperfections.
2. Selection of Edge Banding Material: Depending on the desired look and performance characteristics, a suitable edge banding material is selected. This can include wood veneer, PVC, ABS plastic, or even metal.
3. Application of Edge Banding: The edge banding material is applied to the edges of the board using a specialized edge banding machine. The machine applies heat and pressure to adhere the edge banding material to the edges of the board, ensuring a secure bond.
4. Trimming: Once the edge banding material is applied, any excess material is trimmed off using a trimming tool or edge banding trimmer to ensure a clean and flush edge.
5. Finishing: The edge-banded board is then sanded and finished to blend the edge banding seamlessly with the surface of the board, resulting in a smooth and uniform appearance.
Edge banding is commonly used in the manufacture of cabinets, countertops, shelving, and other furniture and cabinetry components to achieve a professional and polished look. It allows manufacturers to create durable and aesthetically pleasing products while also providing protection to the edges of the boards.
FAQs
What does the wood industry include?
This includes activities such as forestry, logging, sawmilling, woodworking, wood processing, and the manufacturing of various wood products such as lumber, plywood, furniture, paper, and more.
In what sectors does the wood industry play a role?
The wood industry plays a vital role in various sectors including construction, furniture production, packaging and renewable energy.
What is wood forestry?
Wood forestry, also known as forestry or silviculture, is the practice of managing forested areas for the sustainable production of timber and other forest products.
Where is the edge band used?
Edge banding is commonly used in the manufacture of cabinets, countertops, shelving, and other furniture and cabinetry components to achieve a professional and polished look.
 +7929688-88-14
+7929688-88-14
 English
English
 Persian
Persian
 Russian
Russian
 Chinese
Chinese


 +7929688-88-14
+7929688-88-14