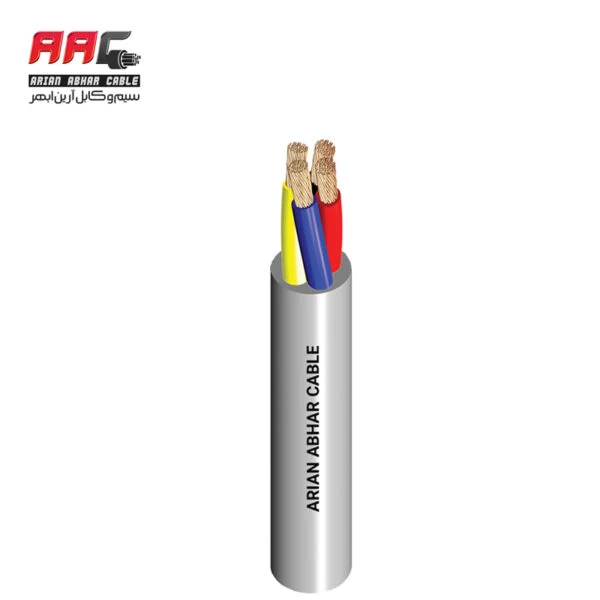
- Test voltage: 3500 volts
- Cable voltage: 450/750 volts
- Production standard: IEC 60245 – CENELEC HD22
- The highest continuous working temperature: 90 degrees Celsius
- Production standard
IEC 60245 - CENELEC HD22 - Cable voltage
450/750 volts - The highest continuous working temperature
90 degrees Celsius - Insulation coloring:
Blue - black brown or blue brown - green and yellow
An electrical cable is an assembly of one or more wires running side by side or bundled, which is used as an electrical conductor to carry electric current.
Most wire will be marked “CU” for copper, the most common conductor of residential electricity. Because electricity travels on the outside of copper wire, these wires are insulated to protect against fire and shock. Aluminum wire is more conductive than copper wire, but it also degrades faster.
A wire is a solid wire that can be single core (solid) or multi-strand (stranded). A cable is two or more insulated wires running together. The main difference is that a wire is a single conductor, while a cable is a group of conductors cabled together under a common jacket.
A power cord, line cord, or mains cable is an electrical cable that temporarily connects an appliance to the mains electricity supply via a wall socket or extension cord.
Electrical cables work by providing a low resistance path for the current to flow through. Electrical cables consist of a core of metal wire offering good conductivity such as copper or aluminium, along with other material layers including insulation, tapes, screens, armouring for mechanical protection, and sheathing.
 +7929688-88-14
+7929688-88-14
 English
English
 Persian
Persian
 Russian
Russian
 Chinese
Chinese


 +7929688-88-14
+7929688-88-14

 Wires, Cables & Cable Assemblies
Wires, Cables & Cable Assemblies









