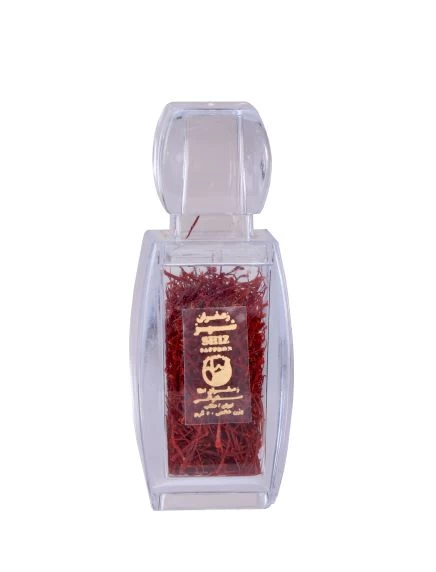
Saffron
Saffron is a highly prized spice that has been revered for its vibrant color, distinct flavor, and various medicinal properties for centuries. It is derived from the delicate stigmas of the Crocus sativus flower, commonly known as the saffron crocus.
This spice is renowned for its rich history, culinary uses, and cultural significance.
Originating in Southwest Asia, saffron has been cultivated and utilized by various civilizations throughout history, including ancient Persians, Greeks, Romans, and Egyptians. It was highly valued by these cultures not only for its culinary applications but also for its use in religious rituals, perfumes, dyes, and medicinal preparations.
The saffron crocus is a unique plant that blooms for a brief period each year, typically during the autumn months. The flowers are delicate and possess vibrant purple petals with three vivid crimson stigmas. These stigmas, often referred to as saffron threads, are carefully handpicked and dried, resulting in the prized spice known as saffron.
Saffron is widely regarded as one of the most expensive spices in the world due to the labor-intensive process involved in its production. It takes a considerable number of flowers to yield a small amount of saffron, as each flower produces only three stigmas. Furthermore, the delicate nature of the stigmas requires meticulous harvesting and drying techniques to preserve their quality.

The distinctive flavor and aroma of saffron are characterized by its earthy, slightly sweet, and floral notes. It adds a unique and exotic taste to a wide variety of dishes, including rice, soups, stews, desserts, and beverages. In many cultures, saffron is a key ingredient in traditional dishes such as Spanish paella, Indian biryani, and Persian saffron rice.
Apart from its culinary uses, saffron has also been valued for its potential health benefits. It contains several bioactive compounds, including crocin, crocetin, and safranal, which contribute to its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and mood-enhancing properties. Saffron has been used in traditional medicine for its potential to alleviate symptoms of depression, enhance cognition, promote digestion, and relieve menstrual discomfort.
In addition to its culinary and medicinal applications, saffron holds cultural and symbolic significance in many regions. It has been associated with royalty, luxury, and prosperity throughout history. In some cultures, saffron has been used in religious ceremonies, weddings, and festivals as a symbol of purity, auspiciousness, and good fortune.
When purchasing saffron, it is essential to ensure its authenticity and quality. Due to its high value, saffron is sometimes adulterated with lower-grade spices or synthetic dyes. Genuine saffron threads are known for their deep red color, distinct aroma, and a slightly bitter taste. It is advisable to obtain saffron from reputable sources to guarantee its purity.
In conclusion, saffron is a treasured spice with a long-standing history and diverse range of uses. Its vivid color, distinct flavor, and potential health benefits have made it a sought-after ingredient in various culinary traditions. Whether it is adding a touch of elegance to a dish or incorporating it into traditional remedies, saffron continues to captivate and inspire people around the world.
Saffron is a versatile spice that is used in a wide range of foods and beverages.
Here are some examples of dishes and culinary preparations where saffron is commonly used:
1. Rice Dishes: Saffron is a key ingredient in many rice-based dishes, such as Spanish paella, Indian biryani, and Iranian saffron rice. It adds a distinct flavor, aroma, and a vibrant golden hue to the rice.
2. Soups and Stews: Saffron is often used to enhance the flavor and color of soups and stews. It can be found in dishes like bouillabaisse (a French seafood stew), Italian risotto, and Moroccan tagines.
3. Desserts and Baked Goods: Saffron is used in a variety of sweet treats and baked goods. It can be found in Indian desserts like kheer (rice pudding) and gulab jamun (sweet dumplings), as well as in Middle Eastern pastries such as baklava.
4. Beverages: Saffron is sometimes used to infuse beverages with its unique flavor and color. It is a popular ingredient in herbal teas, including saffron-infused tea. Saffron is also used in traditional drinks like Indian saffron milk, Spanish saffron-infused liqueurs, and Persian saffron-infused sherbets.
5. Sauces and Condiments: Saffron is often used to enhance the flavor and appearance of sauces and condiments. It can be found in creamy sauces like aioli and bechamel, as well as in condiments like saffron-infused mayonnaise or saffron-infused vinaigrettes.
6. Ice Cream and Puddings: Saffron is occasionally used in ice creams and puddings to provide a distinct flavor and a vibrant yellow color. It adds a touch of luxury and uniqueness to these desserts.
It's important to note that saffron is used sparingly in most recipes due to its potent flavor and high cost. A little goes a long way, and it's usually added towards the end of the cooking process to fully infuse the dish with its aroma and color.
saffron has been associated with several potential health benefits when consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
Here are some of the health benefits that have been attributed to saffron:
1. Antioxidant Properties: Saffron contains several bioactive compounds, including crocin and crocetin, which possess antioxidant properties. Antioxidants help protect the body against oxidative stress and damage caused by free radicals, which are implicated in various chronic diseases.
2. Mood Enhancement: Saffron has been traditionally used to promote a positive mood and alleviate symptoms of mild to moderate depression. Some studies have suggested that saffron may have antidepressant properties and may help improve mood by influencing neurotransmitters in the brain.
3. Cognitive Function: Preliminary studies have indicated that saffron may have potential benefits for cognitive function and memory. It has been suggested that saffron's antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties could contribute to its positive effects on brain health.
4. Eye Health: Saffron has been associated with potential benefits for eye health. It contains compounds, including crocin, that may help protect the retina from damage caused by age-related macular degeneration and oxidative stress.
5. Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Some research suggests that saffron may possess anti-inflammatory properties. It may help reduce inflammation in the body, which is associated with various chronic conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
6. Appetite Suppression: Saffron has been studied for its potential effects on appetite and weight management. Some evidence suggests that saffron may help suppress appetite, reduce snacking, and contribute to weight loss.

It's important to note that while saffron shows promise in these areas, further research is needed to fully understand its mechanisms of action and to determine the optimal dosage and long-term effects. Additionally, saffron should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice or treatment. If you have any specific health concerns, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant dietary changes.


FAQs
How is saffron harvested and processed?
Saffron is harvested by hand, with the delicate stigmas of the saffron crocus flower carefully plucked. The stigmas are then dried to preserve their flavor and potency.
What are the culinary uses of saffron in different cultures?
Saffron is used in a variety of dishes worldwide, including rice dishes, soups, stews, desserts, and beverages, to add flavor, aroma, and vibrant color.
What potential health benefits are associated with consuming saffron?
Consuming saffron is associated with potential health benefits such as antioxidant properties, mood enhancement, cognitive function support, eye health, anti-inflammatory effects, and potential appetite suppression.
How can one ensure the authenticity and quality of saffron when purchasing it?
To ensure the authenticity and quality of saffron, look for reputable sources, check for deep red color, distinct aroma, and slightly bitter taste in the saffron threads, and avoid purchasing saffron that is adulterated with lower-grade spices or synthetic dyes.
 +7929688-88-14
+7929688-88-14
 English
English
 Persian
Persian
 Russian
Russian
 Chinese
Chinese


 +7929688-88-14
+7929688-88-14







.webp)
























