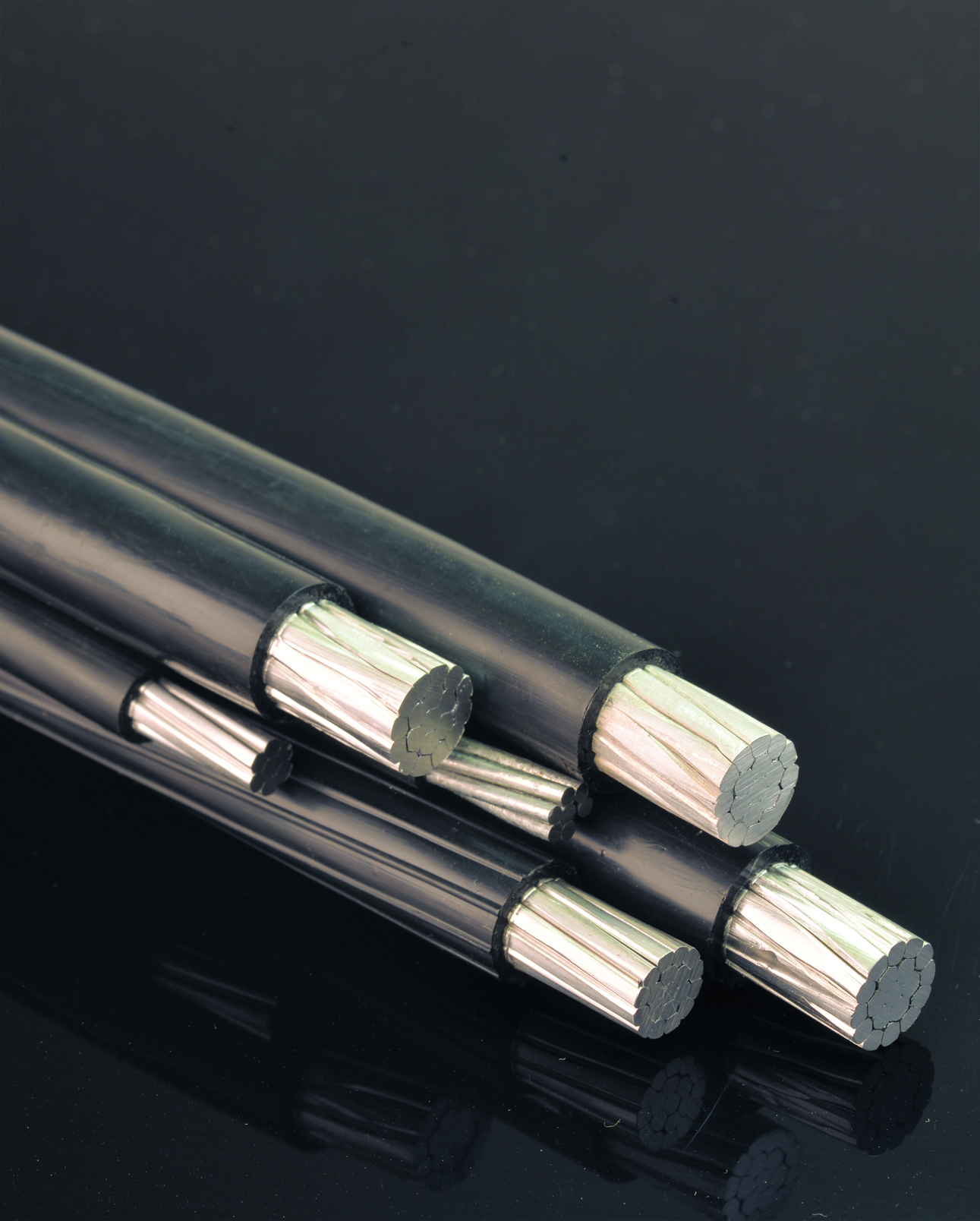
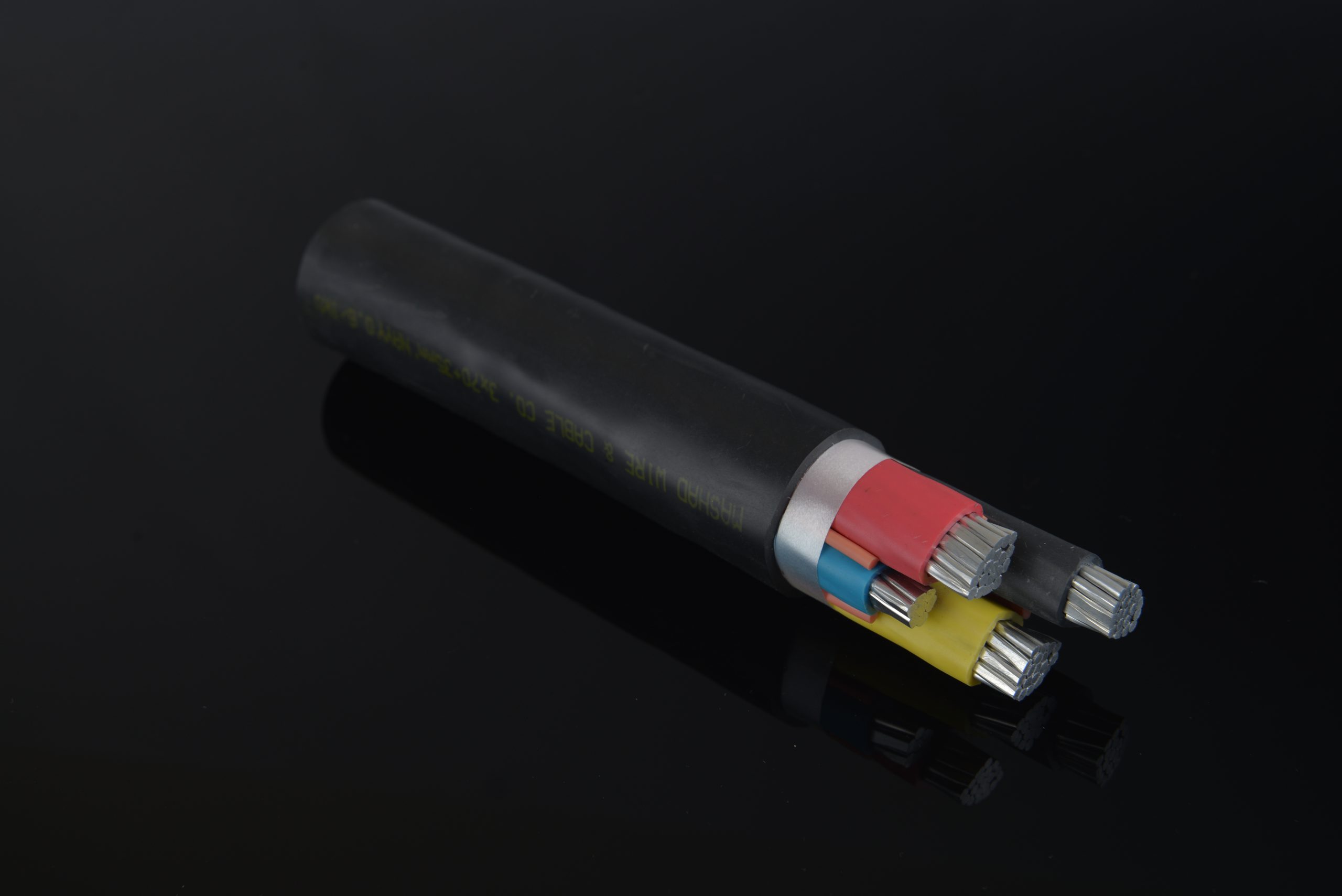
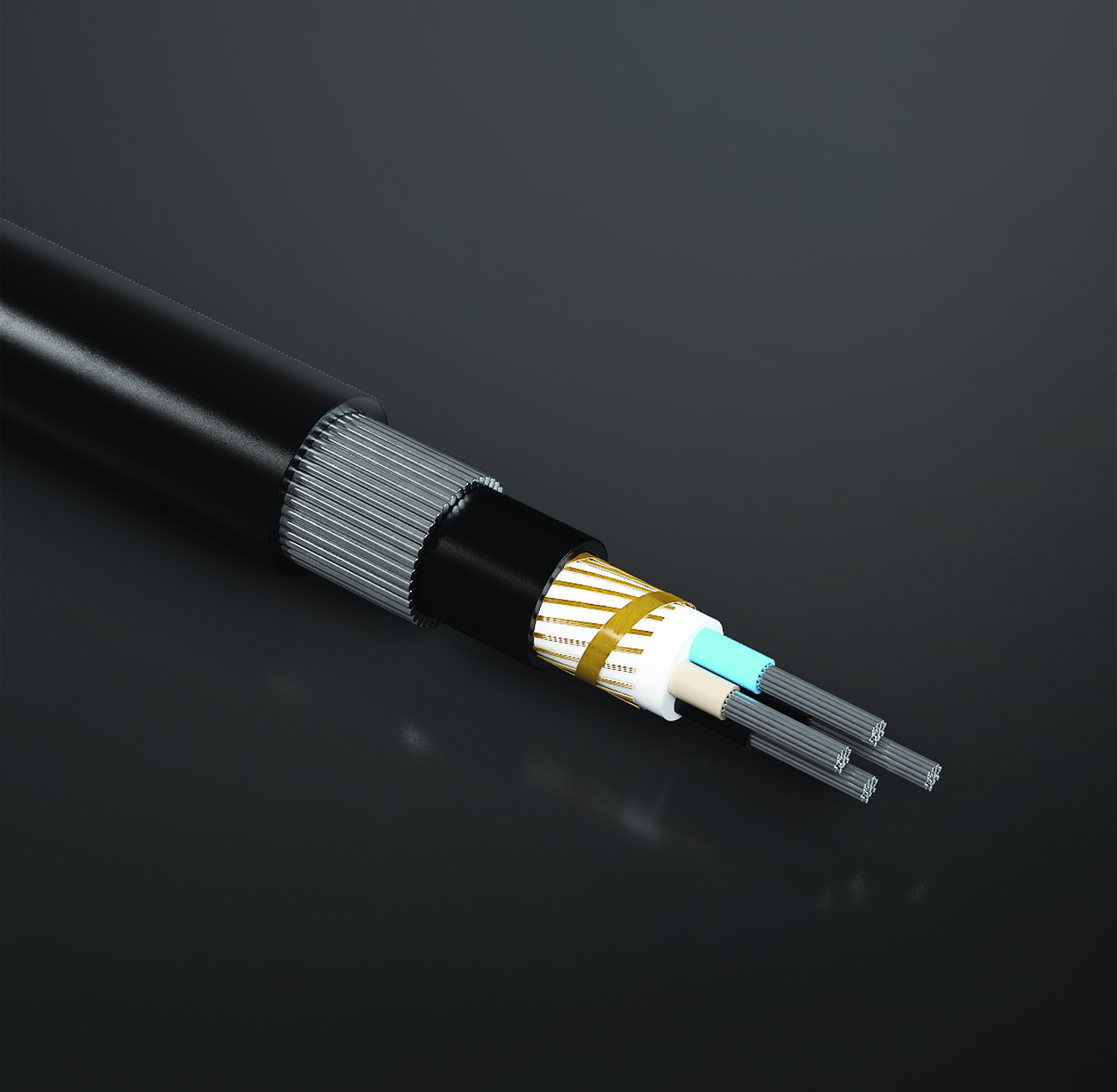
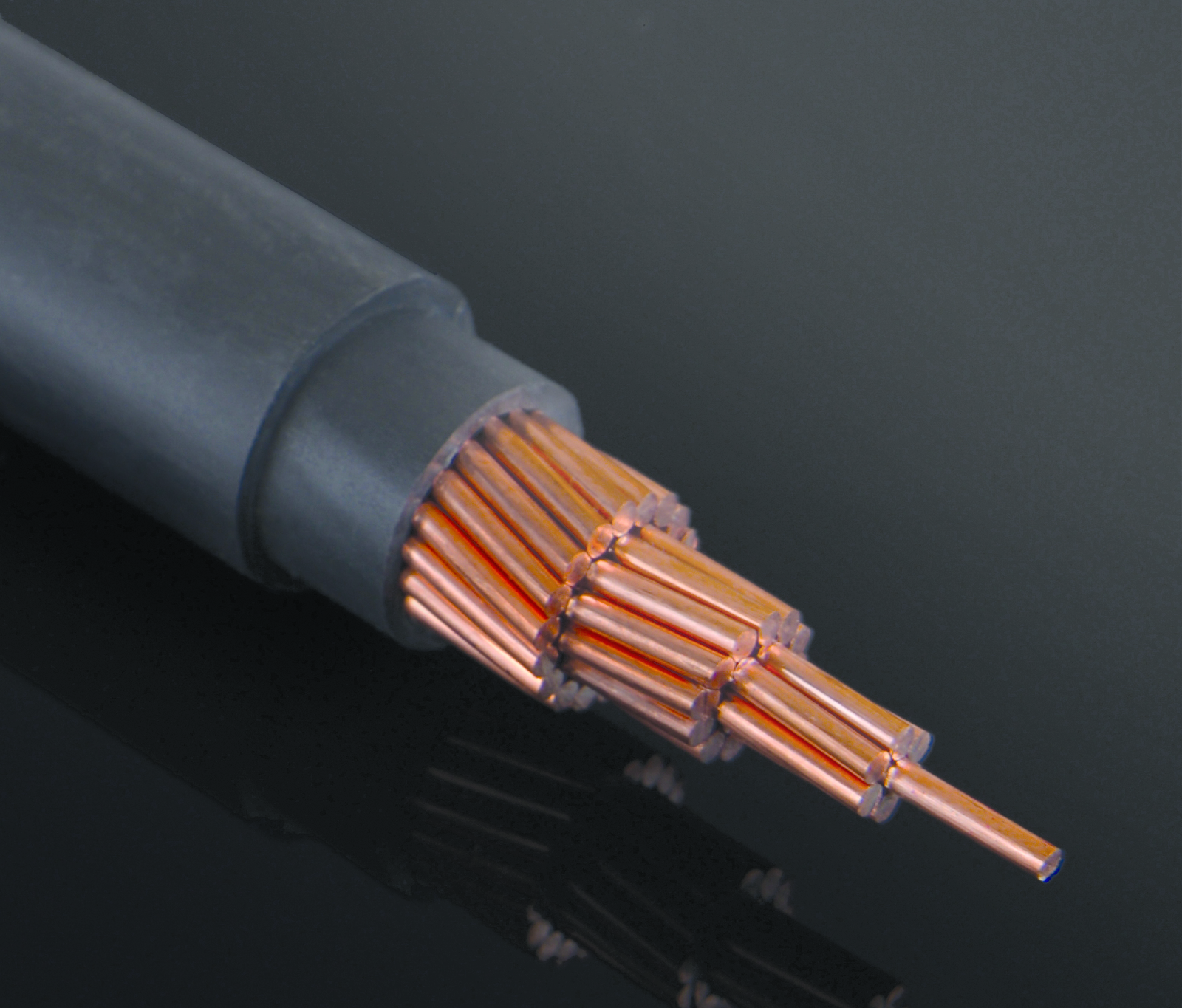
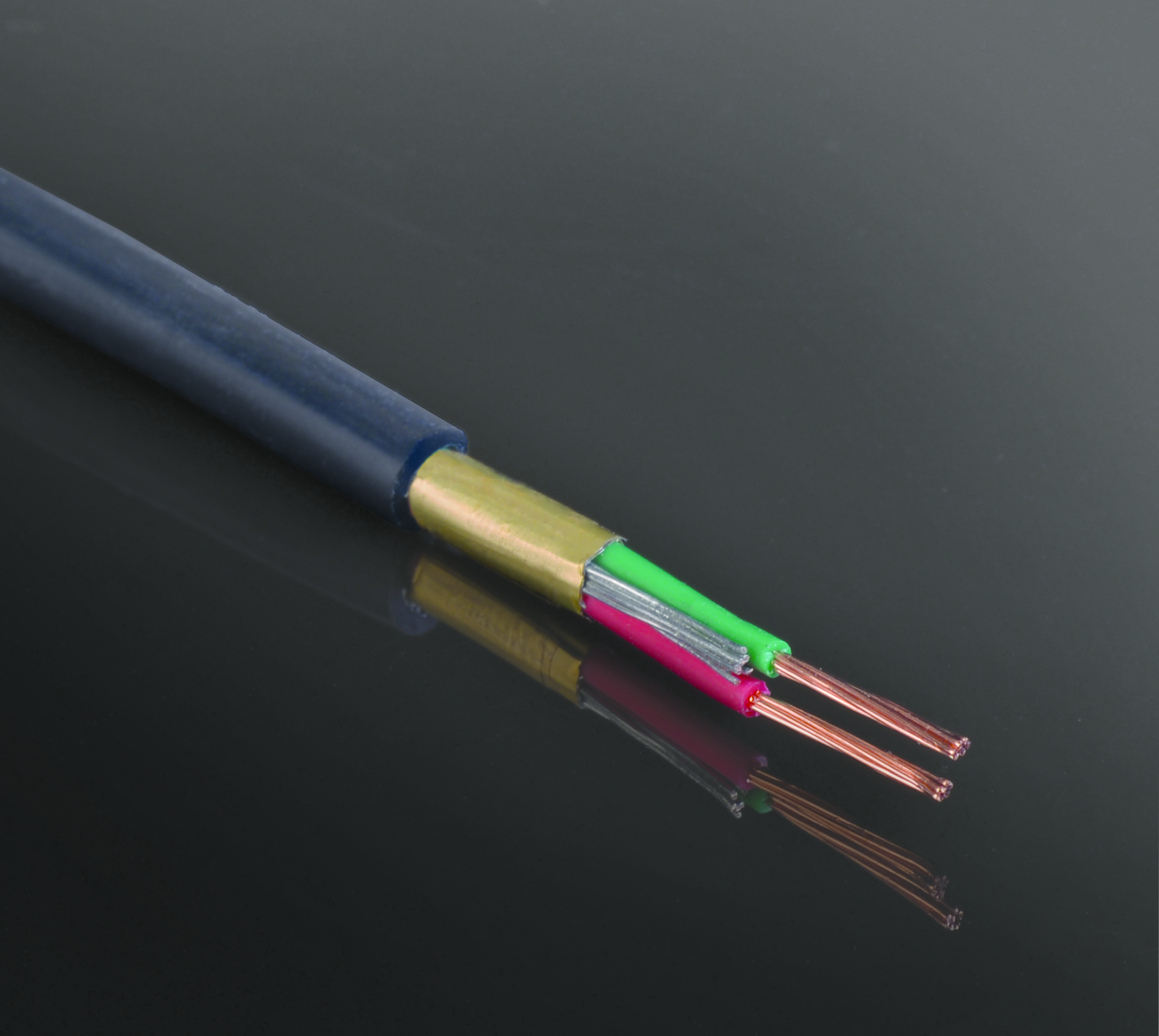
Typically, the voltage of high voltage cables ranges from 63 kV to 132 kV. These cables are made of copper and aluminum. The voltage of transmission line cables ranges from 230 to 500 kW, and in Iran the voltage ranges from 230 to 400 kW.
High voltage copper cables or power cables are used to transmit electrical energy from power plants to central networks or primary distribution networks in systems with rated voltages above 30 kV. They are used as buried underground or in pipelines. New high voltage cable systems are more suitable compared to high voltage cable overhead lines. New industrial methods enable the coordination of submarine high voltage copper cables with optical fibers and provide longer flexible joints than before.
High voltage copper cables use cross-linked polyethylene insulation and CCV line to cover the conductor. The cross-linked polyethylene insulation must have a completely uniform crystal structure without any impurities or defects. The inner and outer semiconducting layers as well as the semiconducting tape are the differences between high voltage cables and low voltage cables and medium voltage cables.
 +7929688-88-14
+7929688-88-14

 Chinese
Chinese
 Persian
Persian
 English
English
 Russian
Russian


 +7929688-88-14
+7929688-88-14

 电线、电缆和电缆组件
电线、电缆和电缆组件